|
abbreviations
"Tr" - a traditional, usually academic definition or symbol
"Ex-" - example
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
MAJOR
1.Tr- large,see Interval. 2.Tr- Form of Triad with the major (large) third placed below the minor (small) third.3.Tr- Form of Mode whose TONIC chord (I) is major.seeModes
MASCULINE RHYME
A cell possesses a MasculineRhymeif its note-value of its Beat remains intact.
MEDIAN
(Tr- third of a chord) seeChordal Function
MELODY
One of the 3 structures of Music, combining Rhythm and Harmony, from whose voice-leading
it evolves, becoming far more sophisticated, the flower of music.
MELO-HARMONY
The choice of harmony (chord pattern) in a melody
MELO-LINES
The choice of Voice-leading Lines (from the chord pattern) in a melody
MELO-RHYTHM
The choice of note-values in a melody MELO-RHYTHM CODE
Abbreviated MRC, this code uses the first letter of the word-name to represent a note-value
-
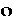 , ,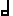 , ,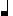 , ,
MELO-RHYTHMIC BOX
A graphic representation of the Melo-rhythm of a specific song, in which each syllable
of the lyrics is placed in its individual compartment.
METAMORPHOSIS
A Transformation in Harmony, in which the analysis of a chord is not the same with
respect to what precedes and with respect to what follows.
MEXICAN 4-CELL REPEAT
A case of repetition of antecedent melodic entities, from the bridge ofMexican Hat Dance(with 4 cells ofII7 / V, II7 / V, II7 / V, II7 / V) MI-MI-MA
A particular form ofEntitycomposed of two small and one large (double-size) part.
MINOR
1.Tr- small,see Interval. 2.Tr- Form of Triad with the major (large) third placed above the minor (small) third.3.Tr- Form of Mode whose TONIC chord (I) is minor. seeModes
MODES
There are 4 strong modes, with a strong DOMINANT-TONIC cadence.
The diatonic Major Mode (with predominantly flattening progressions),
the most common and the most fundamental.
The diatonic Minor Mode (with predominantly sharpening progressions),
an exact inversion of the diatonic Major Mode.
The chromatic Minor Mode (with predominantly flattening progressions), the most
common minor mode.
The chromatic Major Mode (with predominantly sharpening progressions), the most
unusual of the four.
MODULATIONS
Sometimes understood as a cadence with its dominant to a chord other than the main
TONIC, a modulation is better defined as a travel to a different circle, a circle
shift. As there are several kinds of modulations like those that change key (ex: the
second theme of the sonata form), those that do not (the bridge of some popular songs),
as well as key changes that occur suddenly, without a modulation (ex: in some trios),
as also, the shifting techniques and processes can vary, MusicNovatory naturally prefers
using more specific terms to describe these different phenomena.
MOTRIX
(Tr- seventh or sixth) seeChordal Function
MRC
SeeMelo-Rhythm Code
MULTIPLICATION
A generative procedure in Melo-rhythm, in which a section is copied, producing the
next-larger rhythmic level. MUSIC
An intuitive natural phenomenon operating in the 3Worldsof Time, Pitch, Energy, and under the 3 distinct and interrelated organization structures
of Rhythm, Harmony, and Melody.
MusicNovatory
An interactive web document presenting the science of theMusicphenomenon in 5 volumes, that include a comprehensive Introduction, a volume for each
of the organization structures of Music (ie. Rhythm, Harmony, Melody), as well as
an extended Applications volume. MUZIKECO
(pronouncedmooziketsoin Esperanto) signifies the essence of music, and is composed of the structures ofRhythm,Harmony, andMelody. MYSTERIES
The word "mystery" is usually defined as "something unknown, unexplained, or incomprehensible
in its nature", but we prefer "a phenomenon which science has not yet elucidated".
|

